For anyone involved in managing a fleet of vehicles, efficiency and performance are key concerns. Fortunately, modern technology offers a powerful tool in the form of the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) port and its connection to telematics data. For modern fleet management, the On-Board Diagnostics system stands as a crucial component, revolutionizing the way we monitor and maintain vehicles. This critical system has transformed fleet vehicles into intelligent entities, providing comprehensive insights through telematics data.
Join us as we explore the significance of OBD-II in fleet vehicles, shed light on its functionalities, and look at the impact of telematics data on fleet management software.
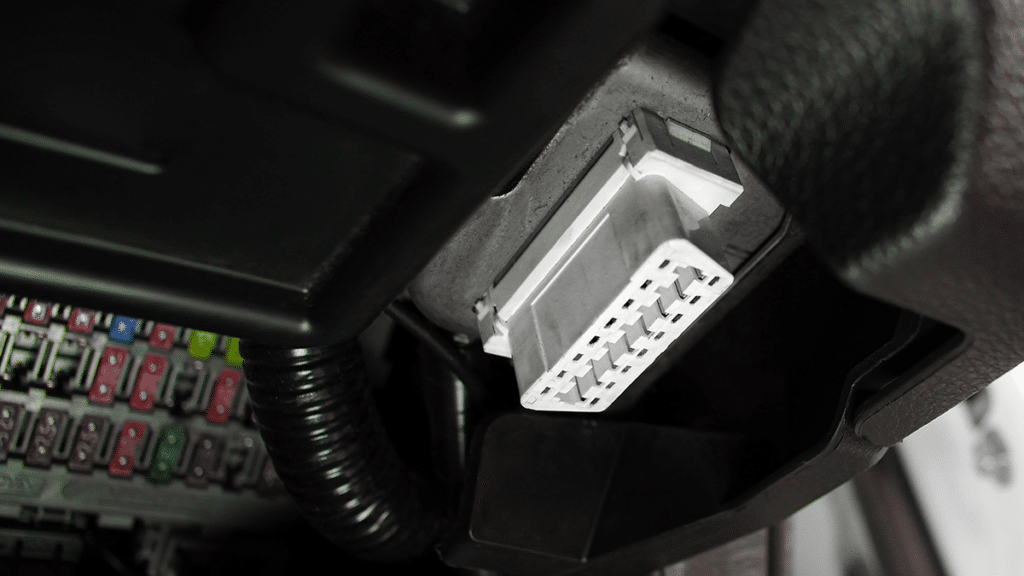

What is OBD?
Imagine your vehicle as a complex organism, constantly monitoring and gathering information about its own health and performance. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) acts as the brains of the vehicle, controlling multiple critical systems, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and idle speed control among others. To control these systems, the ECU collects data from various sensors (e.g., oxygen, coolant temperature, and camshaft position) and makes changes when necessary so that the vehicle can perform as expected.
While collecting this data, the ECU monitors vehicle performance and emission control systems, and stores detected issues as a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). This is where the OBD system comes into play. This data collection and control are essential for the OBD system, which is the standard protocol used across most light-duty vehicles to retrieve vehicle diagnostic information.
By connecting devices through the OBD port, these DTCs can help identify problems that could affect emissions, similar to how a doctor diagnoses a human patient. However, it can also be used to diagnose other mechanical problems with the vehicle, as well as capture additional vehicle data.
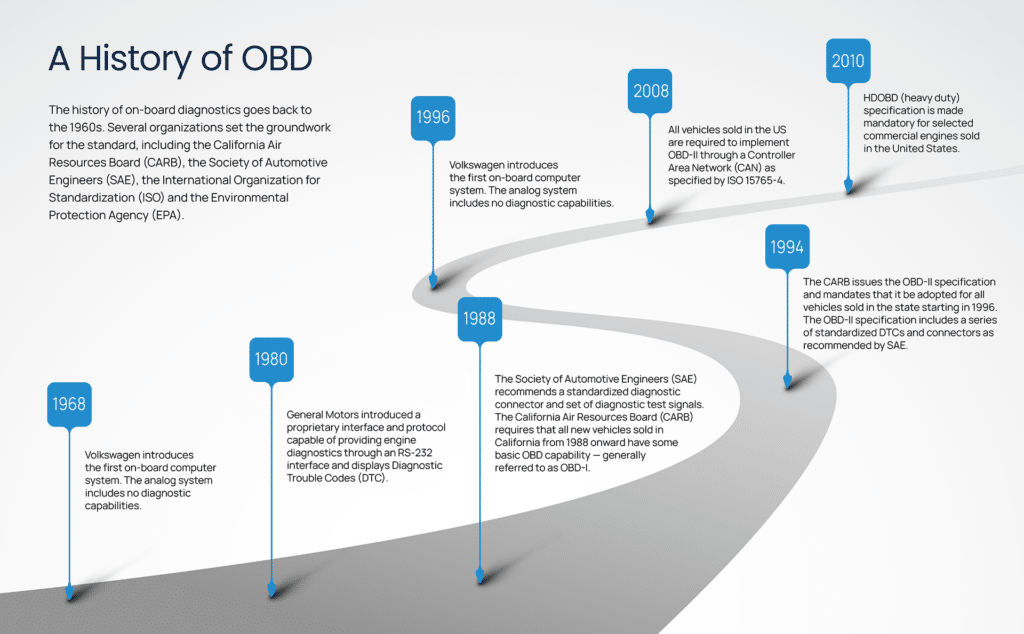
But OBD wasn’t always an option. Back in the old days, mechanics relied on their experience, intuition, and a fair amount of guesswork to figure out what was wrong with a car. Then came the 70s, which brought us disco, Star Wars, and stricter emission regulations. The latter of which led to the birth of OBD in the U.S., which mainly focused on monitoring emissions-related systems.
While a major step forward toward cleaner vehicles, the original OBD system was limited to monitoring only a few emissions-related components as well as a specific level of emissions performance. As technology advanced, the humble OBD platform evolved into OBD-II, which addressed these shortcomings and established a standardized protocol to communicate with emissions control systems across different car manufacturers. By standardizing the diagnostic connector (the port you see under your steering wheel) and the data format, mechanics could use scanning tools across different cars. Today, it goes far beyond emissions, providing a wealth of information about your vehicle.
Capturing Data Through OBD-II in Fleet Vehicles
The OBD-II system has evolved into a comprehensive diagnostic tool for vehicles, as well as a critical component of telematics and fleet management. The ECU constantly monitors various vehicle components and sensors, such as the powertrain and emissions control systems, and marks down any errors detected. By capturing those DTCs, fleet managers can address issues before they escalate into major problems. For fleet managers, this approach to vehicle health minimizes downtime and streamlines emissions compliance.
Telematics devices connected to the OBD-II system, however, can capitalize on the wealth of additional vehicle data available, including a vehicle’s speed, fuel levels, engine RPMs, odometer readings, and much more. By accessing this rich stream of data, fleets can measure and manage multiple aspects of both vehicle health and driving behaviors.
So, what exactly can tapping into the ECU through the OBD-II port tell you? It’s like having a live feed of your car’s internal workings. You can see things like:
- Engine performance: Engine speed, fuel consumption, RPM, emissions levels, fuel consumption, intake air temperature, and more.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC): Error messages that mechanics use to diagnose problems and, more importantly, identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Vehicle usage: Recording data on mileage, driving behavior, and location.
Unlocking the Power of Telematics
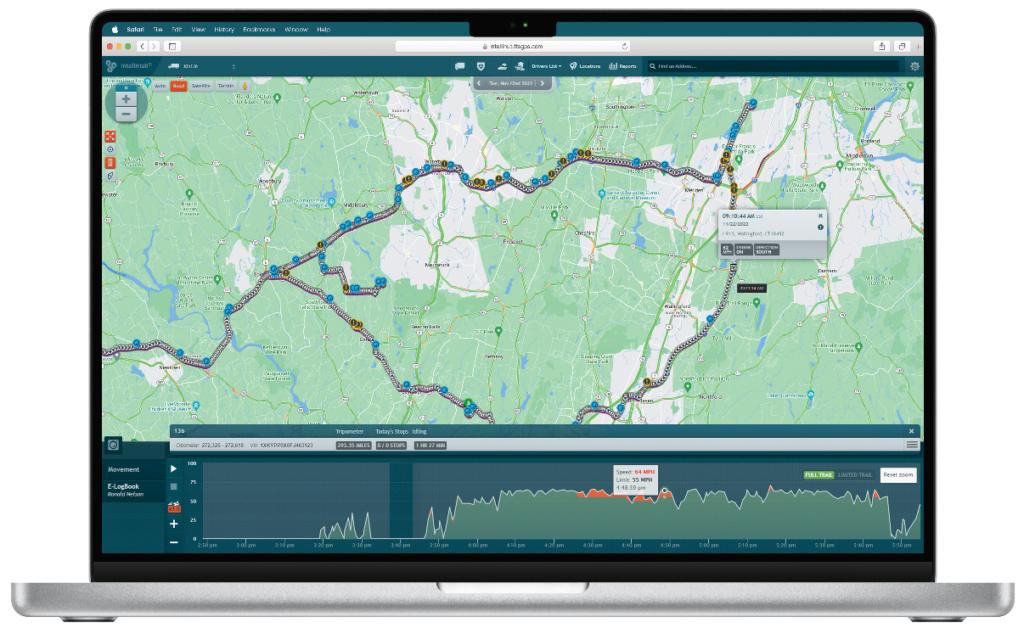
One of the key breakthroughs facilitated by OBD-II in fleet management is the collection of telematics data. Telematics systems act as interpreters, translating and sending the raw data collected by the OBD-II system into actionable information for fleet managers. This valuable data is efficiently transmitted through wireless communication systems (usually in the form of cellular data) from the vehicle to a cloud-based fleet management system, where the information can be accessed through a user-friendly interface.
Through OBD-II, fleet managers gain access to critical insights that go beyond vehicle diagnostics. They can monitor engine RPM, odometer readings, fuel levels, and engine run-time. This wealth of information allows for a comprehensive understanding of each driver’s behavior and aids in optimizing fleet performance.

Here are some key ways telematics data from OBD-II systems benefits fleet management:
Scheduled Maintenance
By monitoring engine parameters and identifying issues early, fleet managers can schedule maintenance before problems escalate. Using this information to stay on top of maintenance issues reduces vehicle downtime and saves on repair costs.
Improved Fuel Efficiency
By using telematics data to track excessive idling, speeding, and harsh acceleration, fleet managers can identify and address fuel-wasting driving habits. Reducing these behaviors through driver training can result in significant fuel savings over time and positively impact both your budget and the environment.
Remote Diagnostics
OBD-II integrated fleet management systems enable remote diagnostics via DTC codes, allowing fleet managers to assess and troubleshoot vehicle issues without requiring physical inspection. This capability saves time and enables faster resolution of problems.
Compliance and Reporting
Telematics data can help ensure compliance with various regulations, such as hours-of-service for drivers. Additionally, it provides valuable data for generating reports and tracking key performance indicators.
The Future of Fleet Management
The evolution of OBD-II systems and telematics has enabled sophisticated data analysis, allowing fleet managers to make data-driven decisions to optimize their operations. To harness the full potential of OBD-II and telematics data, fleet managers can turn to advanced fleet management software, such as IntelliHub. These software solutions act as a centralized hub for monitoring and analyzing the information gathered from the fleet, displaying comprehensive vehicle data and generating insightful analytics reports.
Traditional vehicle GPS trackers have long used OBD-II ports to access this wealth of vehicle data. However, advanced dash cameras, such as FleetCam Pro, integrate both GPS and OBD-II data capture capabilities into a single device, representing a bright future for fleet management tools.
FleetCam Pro, an industry-leading dashcam and video telematics system, utilizes OBD-II technology to provide a comprehensive fleet management solution. This AI-driven dashcam seamlessly integrates with a vehicle’s OBD-II system, capturing a wealth of data and transforming it into actionable insights through IntelliHub, FTS’ connected fleet management platform. IntelliHub allows fleet managers to monitor their entire fleet from a single dashboard, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions that drive success.
By embracing the power of integrated OBD-II telematics, fleet managers can unlock a new level of control and efficiency. With the right tools and data, you can optimize operations, improve driver safety, and achieve significant cost savings.